Diagnostic Tests
1. Chorionic Villous Sampling (CVS)
Chorionic Villous Sampling (CVS) – CVS is performed 11 weeks onwards, in the first trimester. In India, the majority of fetal medicine centres perform CVS per abdomen. It is an ultrasound-guided procedure, using a needle to collect small tissue from the placenta. Since the placenta and fetus are formed from the same cell, the genetic make-up of the placenta represents that of the fetus. There may be mosaicism in 1% of cases, that is there are two different cell lines in the placenta, and the fetal chromosomal pattern may be different from the placental. The procedure-related risk of miscarriage is about 1 in 450 above the background risk of miscarriage. If combined FTS is screen-positive for Down syndrome, women may opt for CVS to confirm the underlying diagnosis.
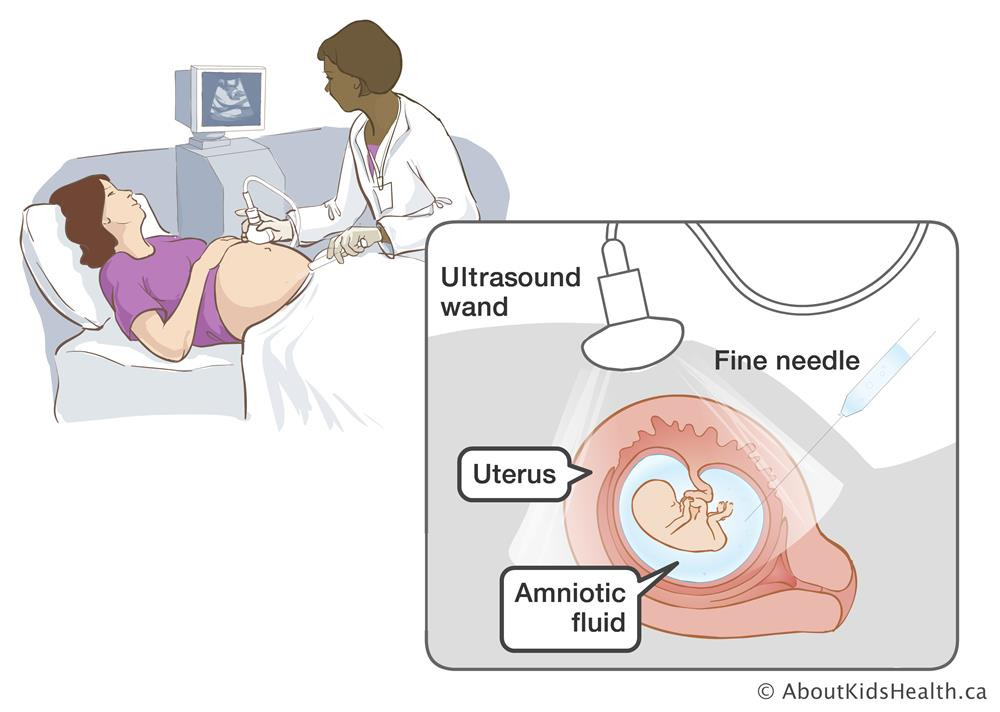
2. Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is performed after the 15th week. It is an ultrasound-guided procedure, performed per abdomen. A small amount of amniotic fluid around the baby is collected for chromosomal analysis. This is more representative of fetal chromosomal pattern, and chances of mosaicism are around 1 in 1000. The procedure-related risk of miscarriage is about 1 in 900 above the background risk of miscarriage.
3. Cordocentesis
Cordocentesis – Cordocentesis means taking a sample from the fetal umbilical cord by directing the needle under ultrasound guidance to the umbilical vein (it is almost always targeted at the point of insertion of the cord in the placenta). In cases where pregnancy is advanced and amniotic fluid is less, cordocentesis can be performed to obtain fetal blood sample for chromosomal analysis. In cases of mosaicism also (on amniocentesis), cord blood sample may be checked for confirmation. Risk of miscarriage or prematurity is around 1% when the procedure is performed after 24 weeks.

